Robust Augmented Reality registration method for Localization of Solid Organs’ Tumors Using CT-derived Virtual Biomechanical Model and Fluorescent Fiducials
Résumé
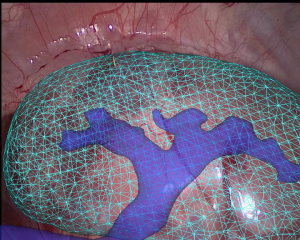
Accurate localization of solid organs tumors is crucial to ensure both radicality and organ function preservation. Augmented Reality (AR) is the fusion of computer-generated and real-time images. AR can be used in surgery as a navigation tool, by creating a patient-specific virtual model through 3D software manipulation of DICOM imaging (e.g. CT-scan). The virtual model can be superimposed to the real-time images to obtain the enhanced real-time localization. However, the 3D virtual model is rigid, and does not take into account inner structures’ deformations. We present a concept of automated navigation system, enabling transparency visualization of internal anatomy and tumor’s margins, while the organs undergo deformation during breathing or surgical manipulation.
Fichier principal
 document.pdf (72.54 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
document.pdf (72.54 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 kars-sages.jpg (135.74 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
kars-sages.jpg (135.74 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |