Influence of Anisotropy on Fluid-Structure Interaction Simulations of Image-Based and Generic Mitral Valves
Résumé
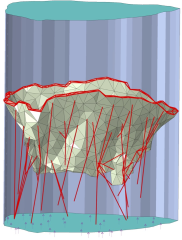
The dynamic behavior of the mitral valve is highly influenced by the material model used to describe the leaflet motion. Due to the presence of collagen fibers, mitral valve leaflets show an anisotropic behavior. The aim of this study is to investigate the influence of anisotropy on fluid-structure simulations of the mitral valve dynamic closure. The fluid-structure simulation of the mitral valve is performed using an immersed boundary method. Two constitutive models, Holzapfel-Gasser-Ogden for the anisotropic, and third-order Ogden for the isotropic are used. For the anisotropic model, two fiber directions, one that is parallel to the annulus surface and another that follows an arc on the leaflets are considered. In order to take into account the effects of both the chordae structure and leaflet geometry, generic and image-based mitral valves are studied. The quality of the closure is evaluated based on measuring the bulging area, contact map, and flow rate. In both generic and imagebased, a significant difference is observed between the anisotropic and isotropic cases. Additionally, The chordae forces during the closure are compared with ex-vivo data of the literature. The results indicate that the anisotropic model with arc-based fibers exhibits a similar pattern.
Domaines
Imagerie médicale
Fichier principal
 FIMH23.pdf (2.84 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
FIMH23.pdf (2.84 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 Case_setup_copy.jpg (148.98 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Case_setup_copy.jpg (148.98 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier

