Data analysis techniques: a tool for cumulative exposure assessment.
Résumé
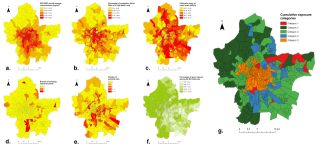
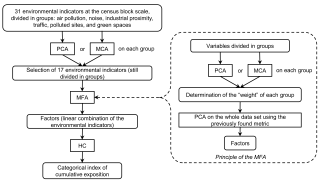
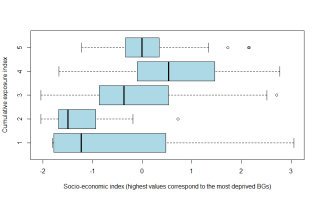
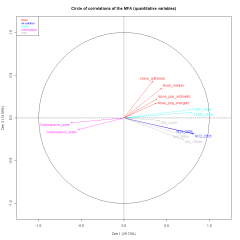
Everyone is subject to environmental exposures from various sources, with negative health impacts (air, water and soil contamination, noise, etc.or with positive effects (e.g. green space). Studies considering such complex environmental settings in a global manner are rare. We propose to use statistical factor and cluster analyses to create a composite exposure index with a data-driven approach, in view to assess the environmental burden experienced by populations. We illustrate this approach in a large French metropolitan area. The study was carried out in the Great Lyon area (France, 1.2 M inhabitants) at the census Block Group (BG) scale. We used as environmental indicators ambient air NO2 annual concentrations, noise levels and proximity to green spaces, to industrial plants, to polluted sites and to road traffic. They were synthesized using Multiple Factor Analysis (MFA), a data-driven technique without a priori modeling, followed by a Hierarchical Clustering to create BG classes. The first components of the MFA explained, respectively, 30, 14, 11 and 9% of the total variance. Clustering in five classes group: (1) a particular type of large BGs without population; (2) BGs of green residential areas, with less negative exposures than average; (3) BGs of residential areas near midtown; (4) BGs close to industries; and (5) midtown urban BGs, with higher negative exposures than average and less green spaces. Other numbers of classes were tested in order to assess a variety of clustering. We present an approach using statistical factor and cluster analyses techniques, which seem overlooked to assess cumulative exposure in complex environmental settings. Although it cannot be applied directly for risk or health effect assessment, the resulting index can help to identify hot spots of cumulative exposure, to prioritize urban policies or to compare the environmental burden across study areas in an epidemiological framework.Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology advance online publication, 24 September 2014; doi:10.1038/jes.2014.66.
Fichier principal
 Article_multiexpo_20140708_c.pdf (830.19 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Article_multiexpo_20140708_c.pdf (830.19 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 Figure_1_-_20140423.png (3.76 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_1_-_20140423.png (3.76 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 Figure_2_-_20140505.png (651.44 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_2_-_20140505.png (651.44 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 Figure_3_-_20140417.png (5.81 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_3_-_20140417.png (5.81 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 Figure_S1_-_20140506.png (13.31 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_S1_-_20140506.png (13.31 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
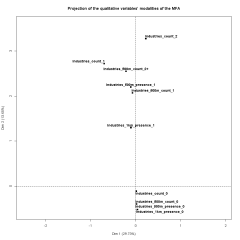 Figure_S2_-_20140506.png (8.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_S2_-_20140506.png (8.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
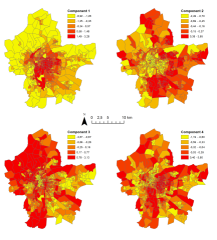 Figure_S3_-_20140507.png (281.34 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_S3_-_20140507.png (281.34 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
Loading...