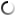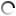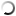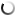Collection des publications de BREED
L’unité mixte de recherche Biologie de la Reproduction, Environnement, Epigénétique et Développement (BREED) étudie les effets de l’environnement au sens large sur la reproduction, le développement au cours de la vie embryonnaire et fœtale et la santé des descendants. Elle associe des chercheurs et des cliniciens hospitaliers et vétérinaires pour des recherches agronomiques et biomédicales.
L’objectif scientifique est de comprendre et maîtriser les mécanismes de programmation épigénétique au cours de la vie anténatale conduisant à la naissance d’un individu en bonne santé, fertile et robuste, capable de s’adapter aux changements de son environnement.
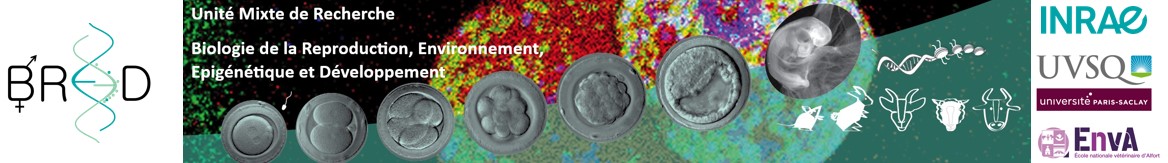
Les finalités de nos recherches sont l’amélioration de la fertilité et de l’efficacité des biotechnologies de la reproduction chez l’homme et l’animal, l’étude des mécanismes physiologiques et moléculaires qui déterminent les phénotypes des descendants (santé, croissance, fertilité, etc) et la recherche de biomarqueurs prédictifs et non invasifs de ces phénotypes, dont certains pourraient compléter les stratégies de sélection génétique chez les animaux. L’unité s’appuie sur des recherches impliquant plusieurs modèles animaux (lapins, ruminants, rongeurs, chevaux) et des approches d’imagerie multiples et complémentaires, qui couvrent de l’échelle microscopique à l’animal entier. Des modèles in vitro sont aussi développés comme alternatives à l’expérimentation animale (cultures cellulaires primaires, organoïdes, embryoïdes). L’ensemble de nos expertises et outils est complété par des études cliniques menées par les praticiens hospitaliers et vétérinaires.
Signature institutionnelle et affiliation HAL
• Pensez à respecter la signature institutionnelle lors de vos publications : Université Paris-Saclay, AP-HP, UVSQ, INRAE, BREED, 78350 Jouy-en-Josas, France
Ecole Nationale Vétérinaire d'Alfort, BREED, 94700 Maisons-Alfort, France
• Pensez à renseigner dans HAL au moment du dépôt l'affiliation au laboratoire présente dans la signature en sélectionnant l'intitulé BREED valide.
• Pensez à renseigner dans HAL au moment du dépôt l'affiliation au laboratoire présente dans la signature en sélectionnant l'intitulé BREED valide.
Il n'est pas nécessaire de saisir les autres éléments (Université Paris-Saclay, UVSQ, INRAE, ENVA) qui sont déjà liés à BREED dans HAL.